Data Extraction - Python APIs for Webscraping and Dumping

Introduction
This post aims at developing two Python APIs for webscraping and data dumping from the following sources -
- Geonames.org
- Data.gov.au
In this blog, we will dive into the fascinating world of extracting data. We will understand what is api and under the hood working of the api’s. Let’s get started!
What is API ?
API stands for Application Programming Interface, is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate and interact with each other.
To use an API, you make a request to a remote web server, and retrieve the data you need. API requests work in exactly the same way - you make a request to an API server for data, and it responds to your request.
Simple illustration of api working :)
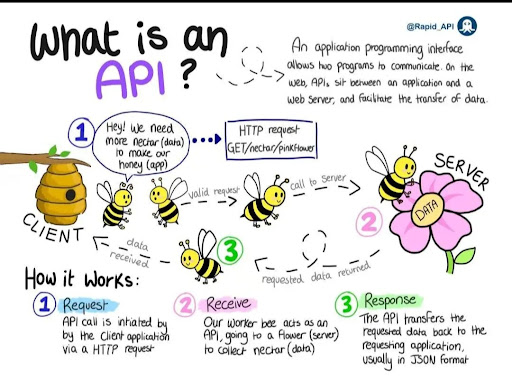
API 1 - From Geonames.org
GeoNames.org is an open-source geographical database available for free. Therefore, I wrote a python api which extracts following data as outputs - Place, postcode, country, state and city in list of dictionaries format. Go to the above website, and click on Browse the names - postal_codes
The github repository for the code - CLICK HERE.
End-Result
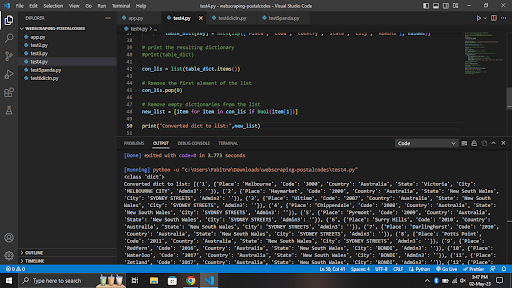
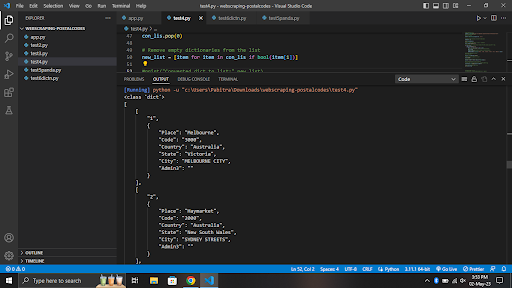
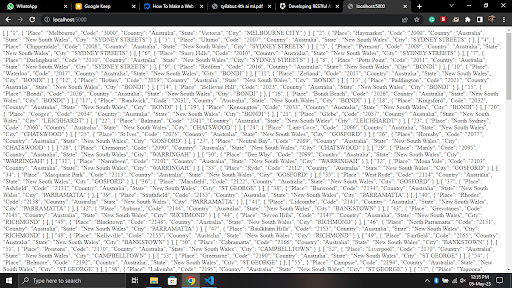
In the api we have used the following -
-
Beautifulsoup - Beautiful Soup is a library that makes it easy to scrape information from web pages. It sits atop an HTML or XML parser, providing Pythonic idioms for iterating, searching, and modifying the parse tree.
-
Json - To get the final output in formatted json string
-
tr = row and td = cell in a table (meaning of tr and td)
-
row.find_all(‘td’) - find_all is method to find all the ‘td’ elements within the row.
API 2 - From Data.gov.au
Data.gov.au is the central source of Australian open government data. Anyone can access the anonymised public data published by federal, state and local government agencies.This data is a national resource that holds considerable value for growing the economy, improving service delivery and transforming policy outcomes. In addition to government data, you can also find publicly-funded research data and datasets from private institutions that are in the public interest.
Go to the above website and search “ G-NAF”. GNAF stands for Geoscape Geocoded National Access File.
Goal -
Our goal is to get postcode, locality and state from this huge dataset.
-
We will import the dataset in our local postgres database
-
We will write python api to extract certain data from our postgres database in list of dictionary format and then covert it into JSON format.
-
We will separate GET/POST method and add error handling in Flask api, so the user will pass postcode and it will return locality and State.
The github repository for the code - CLICK HERE.
End-Result
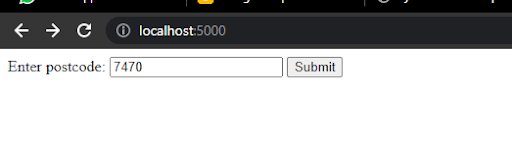
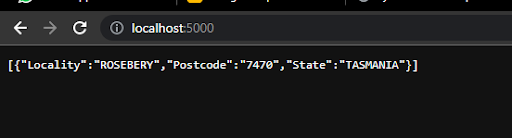
Procedure -
- Download the G-NAF zip file.
- Install postgres SQL in your local computer and set it up.
- Grant permission and run the table creation command by following the pdf guide.
- Here are the list of Tables available -
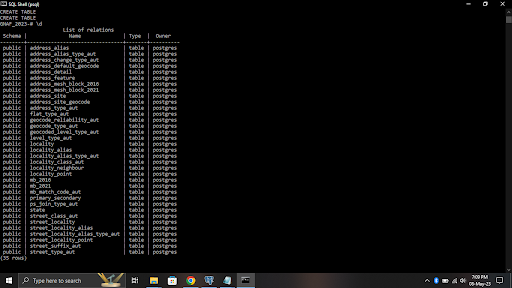
Right now all the tables are empty. We will primarily focus on 3 tables - Address_detail b. Locality c. state
- We will import data in the following table from the zip file we downloaded Here is the command for inserting data in tables from zip file -
| \copy mytable FROM ‘/path/to/mydata.csv’ DELIMITER ‘ | ’ CSV HEADER; |
The zip file has psv file format. PSV means ‘Pipe separated Value”
- By using Join clause we will merge the 3 table attributes in a single table which will give output postcode, state and locality. Join clause is very important, I got to know the importance of JOIN while working for this project. Here is Query result -
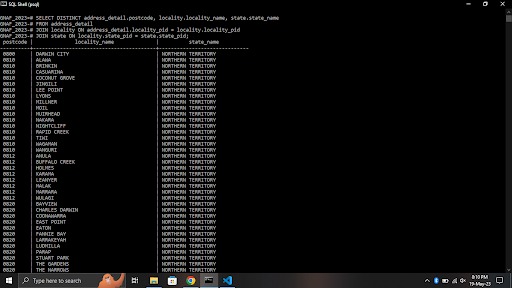
- Finally , the python api will access the postgres database and return the output of postcode, state and locality in list of dictionary format.
I hope this helps! :)
Any Queries, Connect with me -
Email - pabitranewjana@gmail.com Github - https://github.com/pabitrajana007 LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/pabitra-jana-a71693196 Twitter - https://twitter.com/Pabitra007jana